The Power of EDI-ERP Integration in Modern Enterprise Management

The intersection of Electronic Data Exchange (EDI) solutions and Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems signifies a strategic alignment that significantly boosts organizational efficiency. For businesses reliant on a well-functioning supply chain, the integration of EDI and ERP is indispensable. EDI facilitates communication with trading partners on the front end, while the ERP system oversees record management at the back end.
This article delves into the intricacies of this integration, shedding light on how it revolutionizes data management, fostering a more cohesive and agile business environment.
What is Electronic Data Interchange?
Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) enables businesses to exchange documents electronically. EDI software converts important documents into standard electronic formats integrated into various data systems.
Today, businesses have to exchange data within their walls and beyond them. By moving enterprises from paper-based to digital format, EDI allows for smoother, almost instant exchange. Moreover, EDI solutions can reduce processing costs, increase transaction speed, and minimize human errors, thus improving partner relationships.
5 Benefits of EDI
- Enhanced Speed: EDI enhances communication efficiency across supply chains, surpassing manual processing by electronically transferring business documents and data, accelerating business cycles.
- Reduced Costs: The heightened speed of business cycles, facilitated by EDI, contributes to improved outcomes throughout the supply chain, spanning procurement, supply, and last-mile delivery. EDI minimizes transportation and storage expenses, diminishing reliance on warehouse space and promoting just-in-time (JIT) logistics.
- Reduced Errors: EDI facilitates precise computer-to-computer data exchange, reducing dependence on paper document exchange and manual data entry. The automated electronic exchange significantly enhances accuracy and diminishes errors in the process.
- Elevated Efficiency: Innovative EDI solutions utilize automation to optimize various processes, enabling businesses to limit labor hours associated with manual processing. This shift in focus towards efficiency is reinforced by increased document accuracy.
- Interconnectedness: EDIs can seamlessly integrate with other enterprise tools and platforms, including ERP systems. This integration ensures that EDI data is not confined to a specialized department but can be seamlessly transmitted to other applications, enriching business insights and analysis.
What is ERP?
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) software is used by businesses to integrate and manage the company’s critical resources, such as human capital, finances, and time. A comprehensive ERP solution creates a single source of information, eliminating varying duplicates and incompatible technology.
ERP integrates features like production, sales, storage management, finances, and HR, enabling different departments to share information smoothly. Typically, the IT software comprises a toolbox of applications that allows for data collection and analysis necessary to manage the organization successfully.
Enterprise Resource Planning solutions utilize multiple data integrity features to ensure data accuracy when consolidating multiple data sources, including automatic data validation, cleaning, and duplicate removal.
5 Benefits of ERP
- Streamlined Processes: ERP systems provide an overarching structure that integrates various processes. This centralization streamlines operations, reduces data duplicates, and makes the organization more agile and responsive.
- Improved Decision-Making: ERP systems offer real-time data and analytics, enabling informed decision-making. With access to accurate, up-to-date information, management can make strategic decisions.
- Enhances Productivity: Automation of routine tasks and workflows within an ERP software minimizes the need for manual intervention, reducing the likelihood of errors and increasing overall productivity and motivation.
- Better Customer Service: Innovative ERP systems often include modules for customer relationship management (CRM). Centralizing customer data provides personalized interactions and quicker response times, leading to improved customer satisfaction.
- Cost Savings: While the initial implementation cost of an ERP system can be substantial, the long-term benefits include cost savings. Streamlined processes, reduced manual efforts, and improved resource allocation will reduce operational costs. Additionally, better inventory management and procurement processes can result in savings through optimized supply chain operations.
EDI vs. ERP – What is the Difference between ERP and EDI?
| EDI | ERP | |
| Scope and Functionality | EDI primarily focuses on the electronic document exchange between trading partners, standardizing document formats. | ERP is a comprehensive software solution that integrates various business processes within an organization. |
| Purpose | EDI aims to improve the efficiency of information exchange between entities. | ERP streamlines internal processes by providing a unified platform for data management. |
| Focus | EDI is primarily external-facing, because it facilitates communication with suppliers, customers, and partners. | ERP is focused internally, addressing the needs of various departments and functions. |
| Interoperability | EDI is designed to be interoperable with different systems, promoting standardized communication. | ERP systems integrate internal processes, consolidating data from various departments into a cohesive platform. |
What is EDI-ERP Integration?
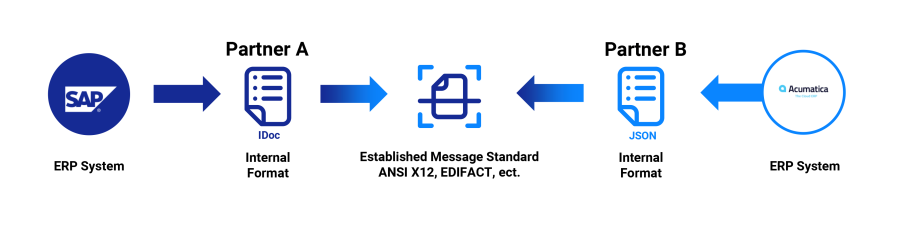
EDI-ERP system integration involves strategically aligning and establishing a seamless connection between the two IT systems, wherein the EDI platform serves as the bridge connecting a company’s ERP system with the entirety of its business areas or the supply chain. While serving distinct functions, these technologies can be effectively integrated to enhance the efficiency and effectiveness of business processes.
In the past, ERP and EDI systems within a company were separate entities, each handling its dedicated processes. Organizations were required to manually input data from one system to another or devise custom integration solutions to automate the data flow. Nowadays, the majority of EDI solutions can be integrated with ERP systems to automate the information flow between applications.
The optimal approach for integrating ERP and EDI is often to leverage middleware solutions in a Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) model. This strategic choice allows companies to entrust the intricate integration process to a secure and modern EDI provider, enabling them to concentrate on the fine-tuning and optimization of their ERP system for enhanced operational efficiency.
Benefits of Integrated EDI and ERP
- Reduced Costs: EDI-ERP integration eliminates human errors, cutting costs and maintaining competitiveness.
- Process Optimization: Automated communication optimizes supply chain operations, including stock, sales projections, and storage.
- Improved Visibility: A single source of truth enhances supply chain visibility, allowing analysis of EDI data with other information using ERP tools.
- Minimized Errors and Compliance Assurance: Commercial EDIs, like Comarch EDI, which includes e-invoicing compliance, contribute to data precision and alignment with regulations, averting potentially costly legal violations.
- Strengthened Vendor and Customer Relationships: Timely and accurate document exchange nurtures improved relationships with both suppliers and customers.
- Scalability: ERP-EDI integration is designed for scalability, which is essential for global businesses with dynamic growth strategies.
- Adaptability to Local Requirements: Integration can be tailored to accommodate specific e-invoicing formats, tax codes, and regulations of each country of operation. Moreover, users have the flexibility to incorporate local EDI specifications without the need for corresponding local ERP specifications.
- Data Analytics and Reporting: Centralized data facilitates analytics and reporting efforts, empowering companies to make well-informed decisions.
- Competitive Advantage: Companies successfully implementing ERP and EDI integration operate more efficiently, adhere to local regulations, and adapt to market changes faster than competitors relying on manual processes.
These benefits are especially valuable to global companies with different ERP environments. For example, some departments may use SAP ECC, while others rely on SAP 3R, and more developed divisions may already have SAP 4/HANA or even a completely different ERP system.
EDI-ERP Integration and Global E-Invoicing Compliance
Today, global companies must consider rapidly changing e-invoicing laws as more and more countries introduce mandatory electronic invoicing and reporting. Each country has its own specific legal requirements regarding formats, mandatory and obligatory data, or technical solutions. Achieving global legal compliance can be challenging, making it crucial to select the right EDI solution provider. Comarch EDI is an integrated platform for electronic data exchange, ensuring compliance with e-invoicing legal regulations in many countries.
EDI-ERP System Integration – Conclusion
Integrating Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) solutions and Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems presents a powerful alliance that transforms how organizations manage data, streamline processes, and navigate the complexities of global business. The seamless connection between these technologies enhances communication with external partners, optimizes internal operations, and ultimately fortifies an organization’s competitive position.
If you’re seeking to integrate EDI with ERP, learn more about Comarch EDI. Schedule a call with our experts today to enhance your business productivity.


